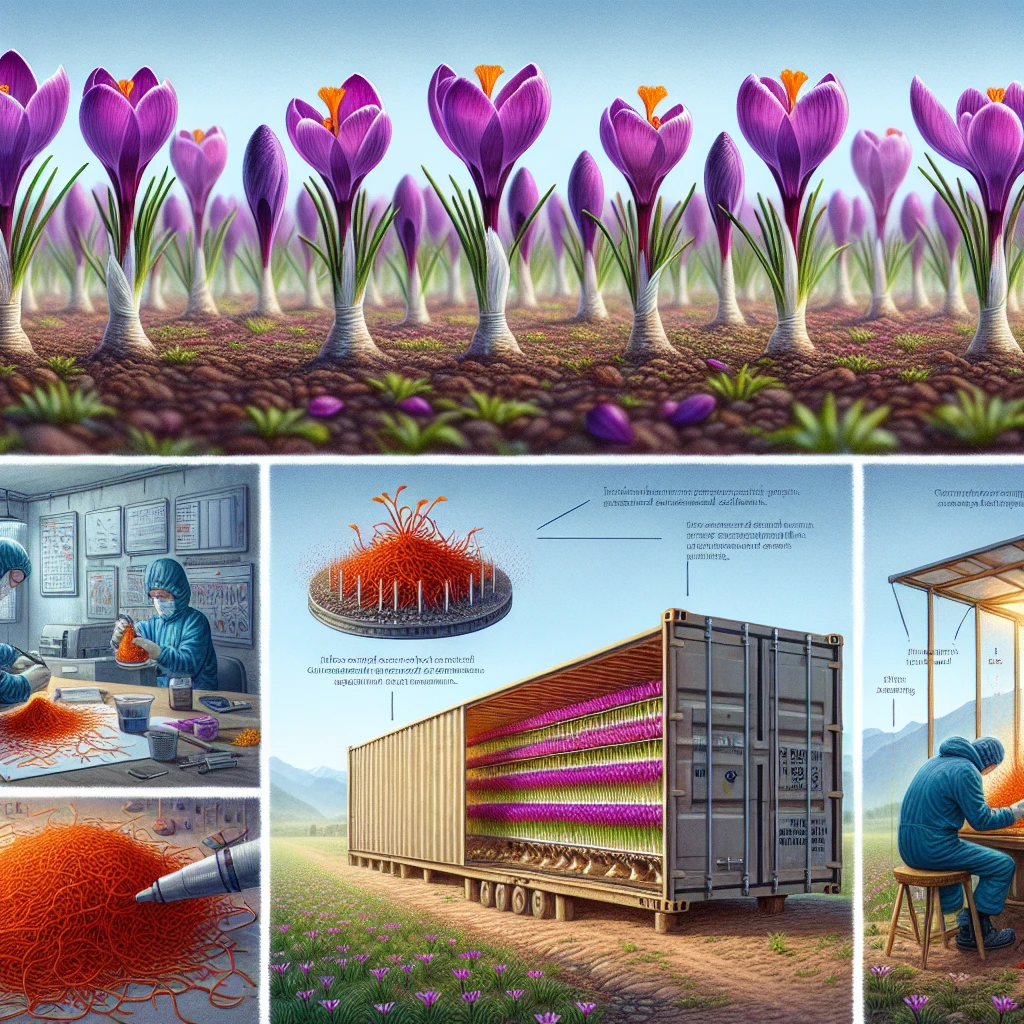
Saffron production in India, which is called “red gold,” is facing some problems that are causing a decrease in how much is made. The town of Pampore in Indian-administered Kashmir is where most of the saffron in the country is made. Saffron is a really valuable spice that costs about $1,500 for every kilo. To make saffron, the red threads called stigma are taken out of the crocus petals and dried. But because the climate is changing, with weird rainfall and hotter temperatures, it’s getting harder to grow saffron. Also, towns and villages are being built on the saffron fields and farmers aren’t getting enough help with things like watering and training, so less saffron is being made.
Scientists are trying to solve these problems by breeding stronger crocus plants that can grow in different climates. They’re using a technique called mutation breeding, where they mess with the DNA of the plants by exposing the seeds to radiation. They hope that some of the changes in the genes will help the plants. They’re also telling farmers how to make their fields better, like planting almond trees with the saffron to give them shade and cool down the soil.
Some farmers are trying new ways to grow saffron. One guy named Shailesh Modak used to work with computers but now he grows saffron. He grows the crocus plants in a big container with air conditioning and a special system to keep the air moving. The plants are grown in tubes with water and nutrients, using a technique called hydroponics. Modak even made software to control all the conditions for growing saffron.
Another idea is to grow the crocus plants inside for part of the year. The corms, which are like the bulbs of the plants, are taken out of the soil and grown inside for three months. Then they’re put back outside just before it’s time to harvest the saffron. Some farmers have had success with this method because it helps protect the plants and makes them grow better.
Even though there are some problems, people are working hard to make saffron production better in India. They want to make sure that this valuable spice can keep being made for a long time.
Original news source: Red gold’: Why saffron production is dwindling in India (BBC)
Listen
Slow
Normal
Fast
Group or Classroom Activities
Warm-up Activities:
– News Summary
Instructions:
1. Divide the students into pairs.
2. Give each pair a copy of the article.
3. Instruct the pairs to read the article and summarize it in 3-5 sentences.
4. After they have completed their summaries, ask each pair to share their summary with the class.
– Opinion Poll
Instructions:
1. Divide the students into small groups.
2. Give each group a list of discussion questions related to the article.
3. Instruct the groups to discuss the questions and share their opinions.
4. After the discussions, ask each group to present their opinions to the class.
– Sketch It
Instructions:
1. Divide the students into pairs.
2. Give each pair a blank piece of paper and a pencil.
3. Instruct one student from each pair to describe a scene from the article to their partner.
4. The partner must then sketch the scene based on the description.
5. After they have completed their sketches, ask each pair to share their drawings with the class.
– Vocabulary Pictionary
Instructions:
1. Divide the students into small groups.
2. Give each group a list of vocabulary words from the article.
3. Instruct the groups to take turns selecting a word and drawing a picture to represent it.
4. The other group members must guess the word based on the drawing.
5. After all the words have been guessed, ask each group to share their drawings with the class and explain the meanings of the words.
– Future Predictions
Instructions:
1. Divide the students into small groups.
2. Instruct each group to discuss and make predictions about the future of saffron production in India based on the information in the article.
3. Encourage the groups to think about the potential solutions mentioned in the article and the impact of climate change.
4. After the discussions, ask each group to present their predictions to the class and discuss their reasoning.
Comprehension Questions:
1. What is causing a decrease in saffron production in India?
2. How much does saffron cost per kilo?
3. What are scientists doing to solve the problems with saffron production?
4. How does mutation breeding work?
5. What are some ways that farmers are trying to grow saffron?
6. Who is Shailesh Modak and what does he do?
7. How does growing the crocus plants inside for part of the year help with saffron production?
8. Why are people working hard to improve saffron production in India?
Go to answers ⇩
Listen and Fill in the Gaps:
(1)______ production in India, which is called “red gold,” is (2)______ some (3)______ that are causing a decrease in how much is made. The town of Pampore in Indian-administered Kashmir is where most of the saffron in the country is made. Saffron is a really valuable spice that costs about $1,500 for every kilo. To make saffron, the red threads called stigma are taken out of the (4)______ petals and dried. But because the climate is changing, with weird rainfall and hotter temperatures, it’s getting harder to grow saffron. Also, towns and villages are being built on the saffron fields and farmers aren’t getting enough help with things like watering and training, so less saffron is being made.
Scientists are trying to solve these problems by breeding stronger crocus plants that can grow in different (5)______. They’re using a (6)______ called (7)______ breeding, where they mess with the DNA of the plants by exposing the seeds to radiation. They hope that some of the changes in the (8)______ will help the plants. They’re also telling farmers how to make their fields better, like planting (9)______ trees with the saffron to give them shade and cool down the soil.
Some farmers are trying new ways to grow saffron. One guy named Shailesh Modak used to work with computers but now he grows saffron. He grows the crocus plants in a big (10)______ with air conditioning and a (11)______ system to keep the air moving. The plants are grown in tubes with water and nutrients, using a technique called hydroponics. Modak even made software to (12)______ all the conditions for growing saffron.
Another idea is to grow the crocus plants inside for part of the year. The corms, which are like the bulbs of the plants, are (13)______ out of the soil and grown inside for three months. Then they’re put back outside just before it’s time to harvest the (14)______. Some farmers have had (15)______ with this method because it (16)______ protect the plants and makes them grow better.
Even though there are some problems, people are working hard to make saffron production better in India. They want to make sure that this valuable spice can keep being made for a long time.
Go to answers ⇩
Discussion Questions:
Students can ask a partner these questions, or discuss them as a group.
1. What is saffron and why is it called “red gold”?
2. How do weird rainfall and hotter temperatures affect the production of saffron?
3. Do you think it’s important to find solutions to the problems facing saffron production? Why or why not?
4. How do scientists hope to solve the problems in saffron production?
5. What is mutation breeding and how does it work?
6. Why do scientists suggest planting almond trees with saffron plants?
7. How does Shailesh Modak grow saffron differently from traditional methods?
8. Do you think growing saffron using hydroponics is a good idea? Why or why not?
9. How does growing the crocus plants inside for part of the year help protect them?
10. Why do you think people are working hard to improve saffron production in India?
11. How would you feel if saffron production continued to decrease and eventually stopped?
12. Do you like saffron? Why or why not?
13. What other valuable spices do you know of? Why are they valuable?
14. How important is it to preserve traditional farming methods? Why or why not?
15. What are some other ways that climate change is affecting agriculture around the world?
Individual Activities
Vocabulary Meanings:
Match each word to its meaning.
Words:
1. saffron
2. valuable
3. climate
4. mutation
5. genes
6. nutrients
7. hydroponics
8. harvest
Meanings:
(a) The act of growing and collecting saffron strands
(b) A method of growing plants without soil
(c) The characteristics passed down from parents to offspring
(d) A process where the DNA of plants is changed
(e) A spice that is very expensive and precious
(f) The weather conditions in a certain area
(g) The act of collecting crops when they are ready
(h) Substances that plants need to grow and be healthy
Go to answers ⇩
Multiple Choice Questions:
1. What is causing a decrease in saffron production in India?
(a) Climate change and urbanization
(b) Lack of demand for saffron
(c) High production costs
(d) Crop diseases and pests
2. What is the cost of saffron per kilo?
(a) $500
(b) $2,000
(c) $1,500
(d) $1,000
3. How are scientists trying to solve the problems in saffron production?
(a) Importing saffron from other countries
(b) Using pesticides to protect the saffron fields
(c) Encouraging farmers to switch to other crops
(d) Breeding stronger crocus plants and providing farming advice
4. What is mutation breeding?
(a) Cross-breeding different plant species to create stronger crops
(b) Using chemicals to enhance plant growth
(c) Growing plants in hydroponic systems
(d) Exposing seeds to radiation to change the DNA of plants
5. What technique did Shailesh Modak use to grow saffron?
(a) Traditional farming methods
(b) Hydroponics
(c) Mutation breeding
(d) Cross-breeding
6. What is the advantage of growing crocus plants inside for part of the year?
(a) It protects the plants and helps them grow better
(b) It increases the yield of saffron
(c) It reduces the cost of saffron production
(d) It allows for year-round saffron production
7. What is the main goal of improving saffron production in India?
(a) Increasing profits for farmers
(b) Ensuring the long-term availability of saffron
(c) Expanding saffron export markets
(d) Reducing the price of saffron for consumers
8. What is the nickname given to saffron in India?
(a) Spice of the gods
(b) Fragrant treasure
(c) Red gold
(d) Indian saffron
Go to answers ⇩
True or False Questions:
1. The town of Pampore in Indian-administered Kashmir is not the main saffron-producing area in the country.
2. Scientists are not using mutation breeding to develop stronger crocus plants that can adapt to different climates.
3. Another method being explored is growing crocus plants indoors for part of the year to protect and enhance their growth.
4. Saffron production in India is facing challenges due to changing climate and urbanization.
5. The process of making saffron involves extracting red threads called stigma from crocus petals and drying them.
6. Some farmers are not experimenting with hydroponics, growing saffron plants in tubes with water and nutrients.
7. Farmers are being advised to plant almond trees alongside saffron to provide shade and cool down the soil.
8. Saffron is an inexpensive spice that costs around $1 per kilo.
Go to answers ⇩
Write a Summary:
Write a summary of this news article in two sentences.
Check your writing now with the best free AI for English writing!
Writing Questions:
Answer the following questions. Write as much as you can for each answer.
Check your answers with our free English writing assistant!
1. Why is saffron production decreasing in India?
2. What are some of the problems that saffron farmers are facing?
3. How are scientists trying to solve the problems with saffron production?
4. What is hydroponics and how is it being used to grow saffron?
5. What is one method that some farmers are using to protect and improve the growth of saffron plants?
Answers
Comprehension Question Answers:
1. What is causing a decrease in saffron production in India?
The changing climate and the construction of towns and villages on saffron fields are causing a decrease in saffron production in India.
2. How much does saffron cost per kilo?
Saffron costs about $1,500 for every kilo.
3. What are scientists doing to solve the problems with saffron production?
Scientists are breeding stronger crocus plants that can grow in different climates using a technique called mutation breeding. They are also advising farmers on how to improve their fields, such as planting almond trees for shade and cooling down the soil.
4. How does mutation breeding work?
Mutation breeding involves exposing the seeds of plants to radiation to induce changes in their DNA. Scientists hope that these changes will help the plants grow better in different climates.
5. What are some ways that farmers are trying to grow saffron?
Some farmers are using hydroponics, where the crocus plants are grown in tubes with water and nutrients. Others are growing the plants inside for part of the year, taking the corms out of the soil and then putting them back outside just before harvest time.
6. Who is Shailesh Modak and what does he do?
Shailesh Modak used to work with computers but now he grows saffron. He has developed a special system with air conditioning and software to control the growing conditions for saffron.
7. How does growing the crocus plants inside for part of the year help with saffron production?
Growing the crocus plants inside for part of the year helps protect them and allows them to grow better. This method provides a controlled environment and safeguards the plants from adverse weather conditions.
8. Why are people working hard to improve saffron production in India?
People are working hard to improve saffron production in India because saffron is a valuable spice and they want to ensure its continued production for a long time.
Go back to questions ⇧
Listen and Fill in the Gaps Answers:
(1) Saffron
(2) facing
(3) problems
(4) crocus
(5) climates
(6) technique
(7) mutation
(8) genes
(9) almond
(10) container
(11) special
(12) control
(13) taken
(14) saffron
(15) success
(16) helps
Go back to questions ⇧
Vocabulary Meanings Answers:
1. saffron
Answer: (e) A spice that is very expensive and precious
2. valuable
Answer: (f) The weather conditions in a certain area
3. climate
Answer: (d) A process where the DNA of plants is changed
4. mutation
Answer: (c) The characteristics passed down from parents to offspring
5. genes
Answer: (h) Substances that plants need to grow and be healthy
6. nutrients
Answer: (b) A method of growing plants without soil
7. hydroponics
Answer: (g) The act of collecting crops when they are ready
8. harvest
Answer: (a) The act of growing and collecting saffron strands
Go back to questions ⇧
Multiple Choice Answers:
1. What is causing a decrease in saffron production in India?
Answer: (a) Climate change and urbanization
2. What is the cost of saffron per kilo?
Answer: (c) $1,500
3. How are scientists trying to solve the problems in saffron production?
Answer: (d) Breeding stronger crocus plants and providing farming advice
4. What is mutation breeding?
Answer: (d) Exposing seeds to radiation to change the DNA of plants
5. What technique did Shailesh Modak use to grow saffron?
Answer: (b) Hydroponics
6. What is the advantage of growing crocus plants inside for part of the year?
Answer: (a) It protects the plants and helps them grow better
7. What is the main goal of improving saffron production in India?
Answer: (b) Ensuring the long-term availability of saffron
8. What is the nickname given to saffron in India?
Answer: (c) Red gold
Go back to questions ⇧
True or False Answers:
1. The town of Pampore in Indian-administered Kashmir is not the main saffron-producing area in the country. (Answer: False)
2. Scientists are not using mutation breeding to develop stronger crocus plants that can adapt to different climates. (Answer: False)
3. Another method being explored is growing crocus plants indoors for part of the year to protect and enhance their growth. (Answer: True)
4. Saffron production in India is facing challenges due to changing climate and urbanization. (Answer: True)
5. The process of making saffron involves extracting red threads called stigma from crocus petals and drying them. (Answer: True)
6. Some farmers are not experimenting with hydroponics, growing saffron plants in tubes with water and nutrients. (Answer: False)
7. Farmers are being advised to plant almond trees alongside saffron to provide shade and cool down the soil. (Answer: True)
8. Saffron is an inexpensive spice that costs around $1 per kilo. (Answer: False)
Go back to questions ⇧