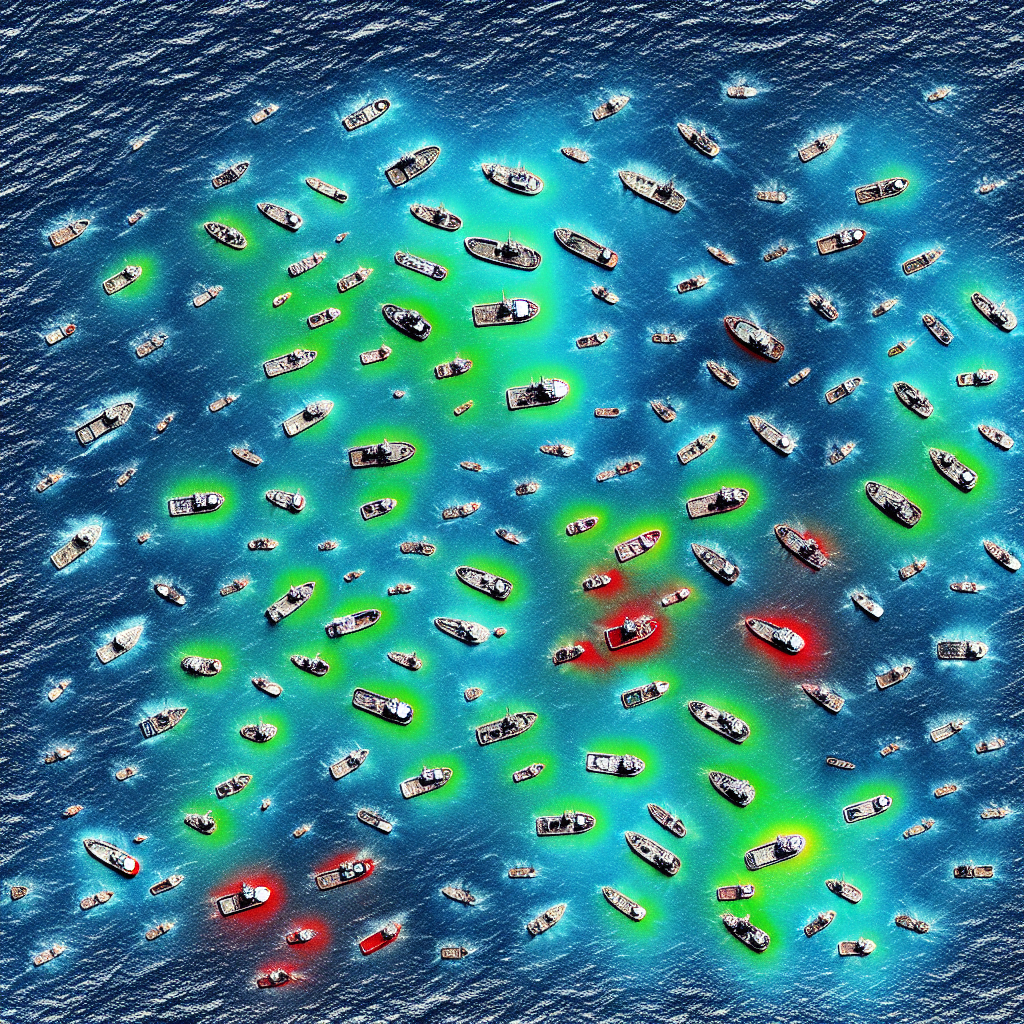
Illegal fishing is a significant problem worldwide, with an estimated 20% of all fish caught being the result of illegal or unregulated fishing. This type of fishing is not only detrimental to marine ecosystems but also contributes to overfishing, with a third of global fish stocks being fished beyond sustainable levels. To combat this issue, organizations like Global Fishing Watch are using artificial intelligence (AI) and satellite imagery to monitor and track the movements of commercial fishing vessels. By analyzing data from vessels’ automatic identification systems (AIS) and combining it with satellite imagery, AI algorithms can identify vessels that are engaged in illegal fishing activities.
Global Fishing Watch’s AI software analyzes millions of gigabytes of satellite imagery to detect vessels and offshore infrastructure. It then cross-references this information with publicly accessible AIS data to identify vessels that are not broadcasting their positions. The AI takes into account various factors such as vessel length, location, density of vessel traffic, and environmental conditions to determine whether a vessel is likely engaged in fishing. This technology has revealed that three-quarters of the world’s industrial fishing vessels are not publicly tracked, particularly in hotspots around Africa and South Asia. Efforts are underway to introduce higher-resolution imagery to better detect smaller fishing vessels.
In addition to AI-based monitoring, other innovative solutions are being developed to combat illegal fishing. For example, a project by the University of Southampton and RS Aqua aims to build a submarine robot equipped with underwater sensors and AI to identify the sound of fishing. This robot would transmit real-time information about fishing activity, particularly within marine protected areas (MPAs), to authorities who can take appropriate action. Currently, less than half of the world’s MPAs are fully protected from fishing, and the robot aims to address this issue by providing timely data to enforce fishing regulations.
The use of AI and other emerging technologies is seen as complementary to traditional law enforcement efforts in combating illegal fishing. However, it is not solely the responsibility of authorities and technology to tackle this problem. Consumers also play a crucial role by making sustainable choices and supporting efforts to crack down on illegal fishing. By raising awareness and demanding sustainable seafood options, individuals can contribute to the preservation of marine ecosystems and the long-term viability of the fishing industry.
Original news source: How AI is being used to prevent illegal fishing (BBC)
🎧 Listen:
Slow
Normal
Fast
📖 Vocabulary:
| 1 | detrimental | Causing harm or damage |
| 2 | ecosystems | Communities of living organisms and their physical surroundings |
| 3 | overfishing | Catching fish at a rate faster than they can reproduce |
| 4 | sustainable | Able to be maintained or continued without harming the environment or depleting resources |
| 5 | artificial intelligence | The simulation of human intelligence in machines |
| 6 | satellite | An object placed into orbit around the Earth to collect information or for communication |
| 7 | algorithms | Step-by-step procedures used for calculations, data processing, and automated reasoning |
| 8 | infrastructure | The basic physical systems of a country, region, or organization |
| 9 | cross-references | Compares and analyzes different sources of information to verify accuracy |
| 10 | density | The measure of how many objects are within a certain area |
| 11 | environmental | Relating to the natural world and the impact of human activity on its condition |
| 12 | hotspots | Areas known for a particular characteristic or activity |
| 13 | resolution | The clarity or detail of an image |
| 14 | submarine | A vessel capable of underwater operation |
| 15 | consumers | Individuals who purchase goods and services for personal use |
Group or Classroom Activities
Warm-up Activities:
– Charades
Instructions: Divide the students into small groups. Give each group a word or phrase related to the article (e.g. illegal fishing, satellite imagery, sustainable seafood). One student from each group will act out the word or phrase without speaking, while the other group members try to guess what it is. The first group to correctly guess the word or phrase gets a point. Rotate the roles so that each student has a chance to act and guess.
– News Summary
Instructions: Have the students read the article individually or in pairs. Then, ask them to summarize the main points of the article in their own words. They can write a short summary or orally present it to the class. Encourage them to include key details and explain why illegal fishing is a significant problem and how technology is being used to combat it.
– Sketch It
Instructions: Divide the students into pairs. Give each pair a key word or phrase from the article (e.g. illegal fishing, AI algorithms, marine protected areas). One student will sketch a visual representation of the word or phrase, while the other student tries to guess what it is. The students can switch roles and continue until they have gone through all the words or phrases.
– Speed Summarizing
Instructions: Divide the students into pairs. Give each pair a timer (e.g. one minute). One student will summarize a section of the article within the given time, while the other student listens and takes notes. Then, they switch roles and repeat the process with a different section of the article. Afterward, have them compare their notes to see how well they captured the main ideas.
– Opinion Spectrum
Instructions: Create a spectrum on one side of the classroom, with one end labeled “Strongly Agree” and the other end labeled “Strongly Disagree”. Ask the students to stand along the spectrum based on their opinions about the statement: “Technology is the most effective solution for combating illegal fishing.” Give them a few minutes to think about their position, and then have them stand along the spectrum, explaining their reasons for their placement. Encourage respectful debate and discussion among the students.
🤔 Comprehension Questions:
1. What percentage of fish caught is estimated to be the result of illegal or unregulated fishing?
2. How does illegal fishing contribute to overfishing?
3. How does Global Fishing Watch use artificial intelligence and satellite imagery to monitor fishing vessels?
4. What factors does the AI software take into account when determining whether a vessel is likely engaged in fishing?
5. What percentage of the world’s industrial fishing vessels are not publicly tracked?
6. What is the purpose of the submarine robot being developed by the University of Southampton and RS Aqua?
7. What percentage of the world’s marine protected areas are fully protected from fishing?
8. What role do consumers play in combating illegal fishing?
Go to answers ⇩
🎧✍️ Listen and Fill in the Gaps:
Illegal fishing is a (1)______ problem worldwide, with an estimated 20% of all fish caught being the result of illegal or unregulated fishing. This type of fishing is not only detrimental to marine ecosystems but also contributes to overfishing, with a third of global fish stocks being fished beyond sustainable levels. To combat this issue, organizations like Global Fishing Watch are using (2)______ intelligence (AI) and satellite imagery to monitor and track the movements of commercial fishing vessels. By (3)______ data from vessels’ automatic (4)______ systems (AIS) and combining it with satellite imagery, AI algorithms can identify vessels that are engaged in illegal fishing activities.
Global Fishing Watch’s AI software analyzes millions of gigabytes of satellite imagery to (5)______ vessels and offshore infrastructure. It then cross-references this information with publicly accessible AIS data to identify vessels that are not broadcasting their (6)______. The AI takes into account various (7)______ such as vessel length, location, density of vessel traffic, and environmental conditions to determine whether a vessel is likely engaged in fishing. This (8)______ has revealed that three-quarters of the world’s industrial fishing vessels are not publicly tracked, particularly in hotspots around Africa and South Asia. Efforts are underway to introduce higher-resolution imagery to better detect smaller (9)______ vessels.
In addition to AI-based monitoring, other innovative solutions are being developed to combat (10)______ fishing. For (11)______, a project by the University of Southampton and RS Aqua aims to build a submarine robot (12)______ with underwater sensors and AI to identify the sound of fishing. This robot would transmit real-time information about fishing activity, particularly within marine protected areas (MPAs), to authorities who can take appropriate action. Currently, less than half of the world’s MPAs are fully protected from fishing, and the robot aims to address this issue by providing timely data to enforce fishing regulations.
The use of AI and other emerging technologies is seen as complementary to traditional law enforcement efforts in combating illegal fishing. However, it is not solely the responsibility of authorities and technology to tackle this problem. (13)______ also play a crucial role by making sustainable choices and supporting efforts to (14)______ down on illegal fishing. By raising awareness and (15)______ sustainable (16)______ options, individuals can contribute to the preservation of marine ecosystems and the long-term viability of the fishing industry.
Go to answers ⇩
💬 Discussion Questions:
Students can ask a partner these questions, or discuss them as a group.
1. What is the impact of illegal fishing on marine ecosystems?
2. How would you feel if you found out that the fish you were eating was caught illegally?
3. Do you think it is important for consumers to make sustainable choices when it comes to seafood? Why or why not?
4. What are some ways that consumers can support efforts to crack down on illegal fishing?
5. How do you think AI and satellite imagery can help in monitoring and tracking fishing vessels?
6. Do you think the use of AI-based monitoring is enough to combat illegal fishing? Why or why not?
7. What are some other innovative solutions that can be developed to combat illegal fishing?
8. How do you think the submarine robot equipped with AI and underwater sensors can help in identifying illegal fishing activity?
9. Do you think it is the responsibility of consumers to demand sustainable seafood options? Why or why not?
10. How can raising awareness about illegal fishing contribute to the preservation of marine ecosystems?
11. What are some challenges in enforcing fishing regulations within marine protected areas?
12. How do you think higher-resolution imagery can help in detecting smaller fishing vessels?
13. Have you ever encountered or heard about any cases of illegal fishing in your country? If so, what were the consequences?
14. Do you like seafood? How do you ensure that the seafood you consume is sourced sustainably?
15. What do you think is the long-term impact of illegal fishing on the fishing industry?
Individual Activities
📖💭 Vocabulary Meanings:
Match each word to its meaning.
Words:
1. detrimental
2. ecosystems
3. overfishing
4. sustainable
5. artificial intelligence
6. satellite
7. algorithms
8. infrastructure
9. cross-references
10. density
11. environmental
12. hotspots
13. resolution
14. submarine
15. consumers
Meanings:
(A) Areas known for a particular characteristic or activity
(B) The simulation of human intelligence in machines
(C) Catching fish at a rate faster than they can reproduce
(D) An object placed into orbit around the Earth to collect information or for communication
(E) Compares and analyzes different sources of information to verify accuracy
(F) Communities of living organisms and their physical surroundings
(G) Step-by-step procedures used for calculations, data processing, and automated reasoning
(H) Relating to the natural world and the impact of human activity on its condition
(I) Individuals who purchase goods and services for personal use
(J) Able to be maintained or continued without harming the environment or depleting resources
(K) The measure of how many objects are within a certain area
(L) The basic physical systems of a country, region, or organization
(M) The clarity or detail of an image
(N) A vessel capable of underwater operation
(O) Causing harm or damage
Go to answers ⇩
🔡 Multiple Choice Questions:
1. What percentage of all fish caught is estimated to be the result of illegal or unregulated fishing?
(a) 20%
(b) 40%
(c) 60%
(d) 80%
2. How much of global fish stocks are being fished beyond sustainable levels?
(a) One-half
(b) Two-thirds
(c) Three-quarters
(d) One-third
3. What does Global Fishing Watch use to monitor and track the movements of commercial fishing vessels?
(a) Artificial intelligence and satellite imagery
(b) Underwater sensors and AI
(c) Traditional law enforcement efforts
(d) Consumer awareness and support
4. What does Global Fishing Watch’s AI software analyze to detect vessels and offshore infrastructure?
(a) Underwater sensors
(b) Satellite imagery
(c) Consumer choices
(d) Law enforcement efforts
5. What does the AI take into account to determine whether a vessel is likely engaged in fishing?
(a) Satellite imagery and underwater sensors
(b) Consumer awareness and support
(c) Traditional law enforcement efforts
(d) Vessel length, location, density of vessel traffic, and environmental conditions
6. Where are three-quarters of the world’s industrial fishing vessels not publicly tracked?
(a) Hotspots around Europe and North America
(b) Hotspots around Australia and South America
(c) Hotspots around Africa and South Asia
(d) Hotspots around Asia and the Middle East
7. What is the aim of the submarine robot project by the University of Southampton and RS Aqua?
(a) To analyze satellite imagery and AIS data to detect illegal fishing vessels
(b) To identify the sound of fishing and transmit real-time information about fishing activity
(c) To raise awareness and demand sustainable seafood options
(d) To enforce fishing regulations in marine protected areas
8. Who plays a crucial role in combating illegal fishing by making sustainable choices and supporting efforts to crack down on it?
(a) Authorities
(b) Technology
(c) Consumers
(d) Marine ecosystems
Go to answers ⇩
🕵️ True or False Questions:
1. Three-quarters of the world’s industrial fishing vessels are not publicly tracked, particularly in hotspots around Africa and South Asia.
2. Efforts are not being made to introduce higher-resolution imagery to better detect smaller fishing vessels.
3. Global Fishing Watch uses artificial intelligence (AI) and satellite imagery to monitor and track commercial fishing vessels.
4. AI algorithms do not analyze data from vessels’ automatic identification systems (AIS) and satellite imagery to identify illegal fishing activities.
5. Consumers can contribute to combating illegal fishing by making sustainable choices and supporting efforts to crack down on it.
6. Approximately 20% of all fish caught globally is a result of illegal or unregulated fishing.
7. Illegal fishing does not contribute to overfishing, with a third of global fish stocks being fished beyond sustainable levels.
8. The University of Southampton and RS Aqua are not developing a submarine robot equipped with AI and underwater sensors to identify fishing activity.
Go to answers ⇩
📝 Write a Summary:
Write a summary of this news article in two sentences.
Check your writing now with the best free AI for English writing!
Writing Questions:
Answer the following questions. Write as much as you can for each answer.
Check your answers with our free English writing assistant!
1. What percentage of fish caught worldwide is estimated to be the result of illegal or unregulated fishing?
2. How does Global Fishing Watch use AI and satellite imagery to monitor and track commercial fishing vessels?
3. What percentage of the world’s industrial fishing vessels are not publicly tracked, according to Global Fishing Watch’s AI software?
4. What innovative solution is being developed by the University of Southampton and RS Aqua to combat illegal fishing?
5. Besides authorities and technology, who else plays a crucial role in combating illegal fishing, according to the article?
✅ Answers
🤔✅ Comprehension Question Answers:
1. What percentage of fish caught is estimated to be the result of illegal or unregulated fishing?
– An estimated 20% of all fish caught is the result of illegal or unregulated fishing.
2. How does illegal fishing contribute to overfishing?
– Illegal fishing contributes to overfishing by exceeding sustainable fishing levels. It is estimated that a third of global fish stocks are being fished beyond sustainable levels.
3. How does Global Fishing Watch use artificial intelligence and satellite imagery to monitor fishing vessels?
– Global Fishing Watch uses AI and satellite imagery to monitor and track the movements of commercial fishing vessels. By analyzing data from vessels’ automatic identification systems (AIS) and combining it with satellite imagery, AI algorithms can identify vessels that are engaged in illegal fishing activities.
4. What factors does the AI software take into account when determining whether a vessel is likely engaged in fishing?
– The AI software takes into account various factors such as vessel length, location, density of vessel traffic, and environmental conditions to determine whether a vessel is likely engaged in fishing.
5. What percentage of the world’s industrial fishing vessels are not publicly tracked?
– Three-quarters (75%) of the world’s industrial fishing vessels are not publicly tracked, particularly in hotspots around Africa and South Asia.
6. What is the purpose of the submarine robot being developed by the University of Southampton and RS Aqua?
– The purpose of the submarine robot being developed by the University of Southampton and RS Aqua is to identify the sound of fishing using underwater sensors and AI. It would transmit real-time information about fishing activity, particularly within marine protected areas (MPAs), to authorities who can take appropriate action.
7. What percentage of the world’s marine protected areas are fully protected from fishing?
– Currently, less than half of the world’s marine protected areas (MPAs) are fully protected from fishing.
8. What role do consumers play in combating illegal fishing?
– Consumers play a crucial role in combating illegal fishing by making sustainable choices and supporting efforts to crack down on illegal fishing. By raising awareness and demanding sustainable seafood options, individuals can contribute to the preservation of marine ecosystems and the long-term viability of the fishing industry.
Go back to questions ⇧
🎧✍️✅ Listen and Fill in the Gaps Answers:
(1) significant
(2) artificial
(3) analyzing
(4) identification
(5) detect
(6) positions
(7) factors
(8) technology
(9) fishing
(10) illegal
(11) example
(12) equipped
(13) Consumers
(14) crack
(15) demanding
(16) seafood
Go back to questions ⇧
📖💭✅ Vocabulary Meanings Answers:
1. detrimental
Answer: (O) Causing harm or damage
2. ecosystems
Answer: (F) Communities of living organisms and their physical surroundings
3. overfishing
Answer: (C) Catching fish at a rate faster than they can reproduce
4. sustainable
Answer: (J) Able to be maintained or continued without harming the environment or depleting resources
5. artificial intelligence
Answer: (B) The simulation of human intelligence in machines
6. satellite
Answer: (D) An object placed into orbit around the Earth to collect information or for communication
7. algorithms
Answer: (G) Step-by-step procedures used for calculations, data processing, and automated reasoning
8. infrastructure
Answer: (L) The basic physical systems of a country, region, or organization
9. cross-references
Answer: (E) Compares and analyzes different sources of information to verify accuracy
10. density
Answer: (K) The measure of how many objects are within a certain area
11. environmental
Answer: (H) Relating to the natural world and the impact of human activity on its condition
12. hotspots
Answer: (A) Areas known for a particular characteristic or activity
13. resolution
Answer: (M) The clarity or detail of an image
14. submarine
Answer: (N) A vessel capable of underwater operation
15. consumers
Answer: (I) Individuals who purchase goods and services for personal use
Go back to questions ⇧
🔡✅ Multiple Choice Answers:
1. What percentage of all fish caught is estimated to be the result of illegal or unregulated fishing?
Answer: (a) 20%
2. How much of global fish stocks are being fished beyond sustainable levels?
Answer: (d) One-third
3. What does Global Fishing Watch use to monitor and track the movements of commercial fishing vessels?
Answer: (a) Artificial intelligence and satellite imagery
4. What does Global Fishing Watch’s AI software analyze to detect vessels and offshore infrastructure?
Answer: (b) Satellite imagery
5. What does the AI take into account to determine whether a vessel is likely engaged in fishing?
Answer: (d) Vessel length, location, density of vessel traffic, and environmental conditions
6. Where are three-quarters of the world’s industrial fishing vessels not publicly tracked?
Answer: (c) Hotspots around Africa and South Asia
7. What is the aim of the submarine robot project by the University of Southampton and RS Aqua?
Answer: (b) To identify the sound of fishing and transmit real-time information about fishing activity
8. Who plays a crucial role in combating illegal fishing by making sustainable choices and supporting efforts to crack down on it?
Answer: (c) Consumers
Go back to questions ⇧
🕵️✅ True or False Answers:
1. Three-quarters of the world’s industrial fishing vessels are not publicly tracked, particularly in hotspots around Africa and South Asia. (Answer: True)
2. Efforts are not being made to introduce higher-resolution imagery to better detect smaller fishing vessels. (Answer: False)
3. Global Fishing Watch uses artificial intelligence (AI) and satellite imagery to monitor and track commercial fishing vessels. (Answer: True)
4. AI algorithms do not analyze data from vessels’ automatic identification systems (AIS) and satellite imagery to identify illegal fishing activities. (Answer: False)
5. Consumers can contribute to combating illegal fishing by making sustainable choices and supporting efforts to crack down on it. (Answer: True)
6. Approximately 20% of all fish caught globally is a result of illegal or unregulated fishing. (Answer: True)
7. Illegal fishing does not contribute to overfishing, with a third of global fish stocks being fished beyond sustainable levels. (Answer: False)
8. The University of Southampton and RS Aqua are not developing a submarine robot equipped with AI and underwater sensors to identify fishing activity. (Answer: False)
Go back to questions ⇧