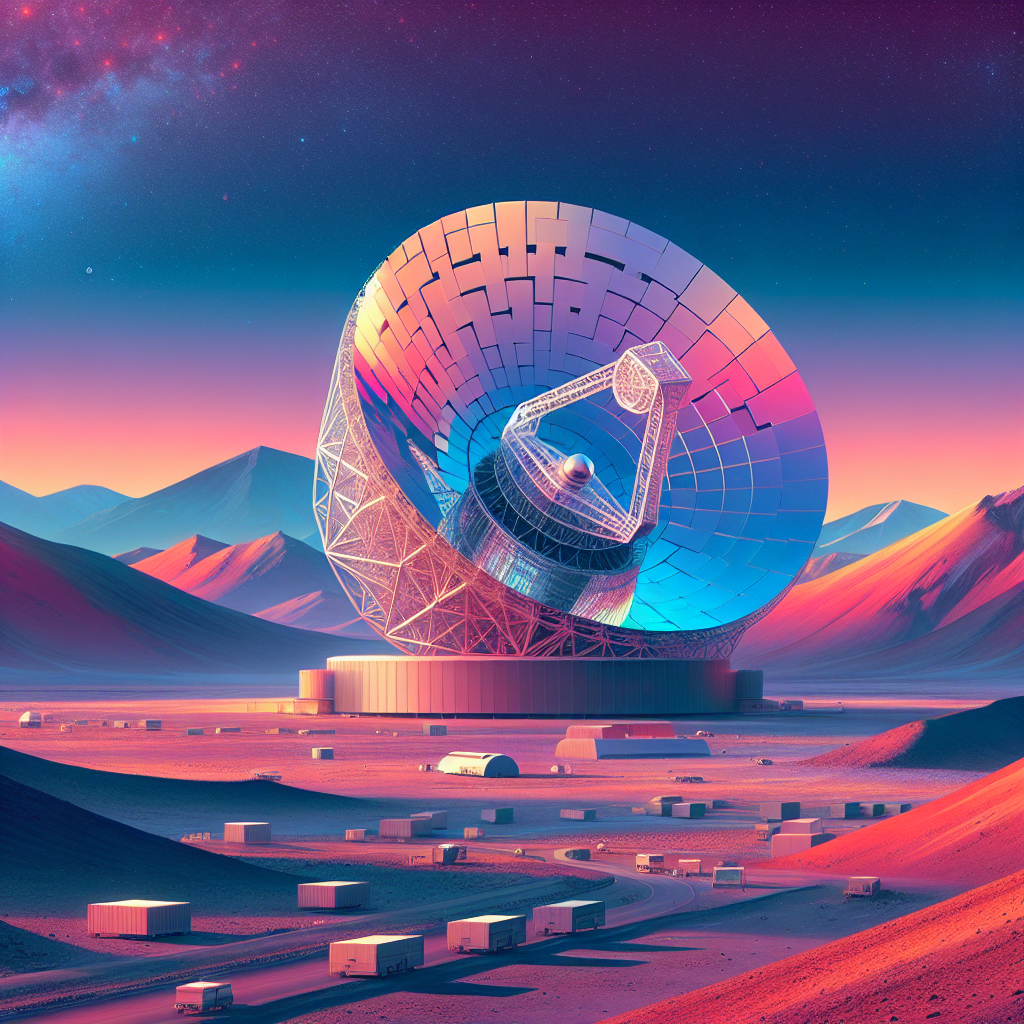
In Chile’s dry Atacama desert, the European Southern Observatory (ESO) is building the Extremely Large Telescope (ELT), which will be the biggest optical telescope globally. It’s expected to start working in 2028 and will change how we see the universe. The ELT has five huge mirrors, with the main mirror, M1, being 39 meters wide and made up of 798 smaller hexagonal pieces that work together as one. These mirrors are super precise and will help us see more of the universe by capturing light from space.
Dr. Elise Vernet, who works at ESO, is in charge of making sure the ELT’s mirrors are top-notch. One cool thing is the M4 mirror, which is the biggest flexible mirror ever made. It can change its shape 1,000 times every second to deal with things like air movements and vibrations in the telescope. Also, the Max Planck Institute for Quantum Optics has made a mirror at the tiniest level possible, showing how quantum tech could be used in the future, like for secure data networks.
Over in Oberkochen, Germany, Zeiss is working on making super flat mirrors that are crucial for machines used in making computer chips. These mirrors help print really small transistors on silicon wafers, making computer chip production more efficient. Zeiss is aiming to create microchips with one trillion transistors by 2030, which is a big jump from what we have now.
The amazing technology behind these advanced mirrors is helping us make more powerful computer chips and discover new things in space and quantum physics. By striving for perfection in mirror design, we are pushing the limits of technology and expanding our knowledge of the universe. Looking forward, it’s clear that mirrors will keep playing a big role in shaping the future of technology that impacts our world.
Original news source: The mind-bending mirrors behind advanced technology (BBC)
🎧 Listen:
Slow
Normal
Fast
📖 Vocabulary:
| 1 | Observatory | A place equipped for observing celestial events |
| 2 | Optical | Related to sight or vision |
| 3 | Hexagonal | Having six sides and six angles |
| 4 | Precise | Exact and accurate |
| 5 | Vibrations | Rapid movements back and forth |
| 6 | Quantum | Relating to the smallest particles of matter |
| 7 | Secure | Safe and protected from danger |
| 8 | Transistors | Small electronic parts that control the flow of electricity |
| 9 | Silicon | A chemical element used in making electronic circuits |
| 10 | Efficient | Working in a way that saves time and energy |
| 11 | Production | The process of making or creating something |
| 12 | Advanced | Highly developed or complex |
| 13 | Striving | Making a great effort to achieve something |
| 14 | Perfection | The state of being free from flaws or defects |
| 15 | Expanding | Increasing in size or scope |
Group or Classroom Activities
Warm-up Activities:
– Headline Creation
Instructions:
1. Divide the students into small groups.
2. Ask each group to come up with a catchy headline summarizing the article about the Extremely Large Telescope and advanced mirror technology.
3. Give them a few minutes to brainstorm and create their headline.
4. Each group presents their headline to the class and explains why they chose it.
– Vocabulary Pictionary
Instructions:
1. Write down key vocabulary words from the article on separate pieces of paper and put them in a bag or container.
2. One student picks a word from the bag and has to draw it on the board without using any letters, numbers, or symbols.
3. The rest of the class tries to guess the word based on the drawing.
4. The student who guesses correctly gets to pick the next word from the bag and draw.
– Think-Pair-Share
Instructions:
1. Ask the students to think individually about the impact of advanced mirror technology on science and technology after reading the article.
2. Pair the students up and have them discuss their thoughts with their partner.
3. After a few minutes, open the discussion to the whole class and ask a few pairs to share their ideas.
4. Encourage the class to add on to each other’s points and have a group discussion.
– Opinion Spectrum
Instructions:
1. Create a line on one side of the classroom with one end labeled “Strongly Disagree” and the other end labeled “Strongly Agree.”
2. Read out statements related to the article about the ELT and advanced mirror technology.
3. Have students physically place themselves along the line based on how much they agree or disagree with each statement.
4. After each statement, allow a few students to explain why they chose their position on the spectrum.
– News Reporter Role-play
Instructions:
1. Divide the class into pairs – one will be the news reporter and the other the interviewee.
2. The news reporter has to come up with questions about the ELT and advanced mirror technology based on the article.
3. The interviewee must answer as if they are an expert in the field.
4. After a few minutes of preparation, each pair performs their role-play in front of the class, with the news reporter asking questions and the interviewee responding.
🤔 Comprehension Questions:
1. What is the name of the telescope being built in Chile’s Atacama desert, and when is it expected to start working?
2. How many huge mirrors does the Extremely Large Telescope (ELT) have, and what are they made of?
3. Who is responsible for ensuring the ELT’s mirrors are of high quality?
4. What is unique about the M4 mirror in the ELT?
5. What is the Max Planck Institute for Quantum Optics working on that involves mirrors?
6. Where is Zeiss located, and what are they working on regarding mirrors?
7. How do super flat mirrors made by Zeiss contribute to computer chip production?
8. How is the technology behind advanced mirrors impacting both computer chip production and the study of space and quantum physics?
Go to answers ⇩
🎧✍️ Listen and Fill in the Gaps:
In Chile’s dry Atacama desert, the European Southern Observatory (ESO) is building the Extremely (1)______ Telescope (ELT), which will be the biggest optical (2)______ globally. It’s expected to start working in 2028 and will change how we see the universe. The ELT has five huge mirrors, with the main mirror, M1, being 39 meters wide and made up of 798 smaller (3)______ pieces that work together as one. These mirrors are super (4)______ and will help us see more of the universe by capturing light from space.
Dr. Elise Vernet, who works at ESO, is in charge of making sure the ELT’s (5)______s are top-notch. One cool thing is the M4 mirror, which is the biggest (7)______ mirror ever made. It can change its shape 1,000 times every second to deal with things like air movements and vibrations in the telescope. Also, the Max Planck (8)______ for Quantum Optics has made a mirror at the tiniest level possible, showing how (9)______ tech could be used in the future, like for secure data networks.
Over in Oberkochen, Germany, Zeiss is (10)______ on (11)______ super flat mirrors that are crucial for machines used in making computer chips. These mirrors help print really small transistors on silicon wafers, making computer chip production more efficient. Zeiss is aiming to create (12)______ with one trillion transistors by 2030, which is a big jump from what we have now.
The (13)______ technology behind these advanced mirrors is helping us make more powerful computer chips and discover new things in space and quantum (14)______. By striving for perfection in mirror (15)______, we are pushing the limits of technology and expanding our (16)______ of the universe. Looking forward, it’s clear that mirrors will keep playing a big role in shaping the future of technology that impacts our world.
Go to answers ⇩
💬 Discussion Questions:
Students can ask a partner these questions, or discuss them as a group.
1. What do you think about the Extremely Large Telescope being built in Chile’s Atacama desert?
2. How would you feel if you could see more of the universe through the ELT’s super precise mirrors?
3. Do you like the idea of a mirror that can change its shape 1,000 times every second like the M4 mirror?
4. What is a quantum tech, and why do you think it could be important for secure data networks in the future?
5. Do you think making super flat mirrors for computer chip production is an important technological advancement?
6. How do you think super flat mirrors can help in printing really small transistors on silicon wafers?
7. Why do you think Zeiss is aiming to create microchips with one trillion transistors by 2030?
8. What are your thoughts on the idea of pushing the limits of technology through mirror design?
9. How important do you think mirrors are in shaping the future of technology that impacts our world?
10. Why do you think mirrors will continue to play a big role in technology advancements in the future?
11. How do you think the technology behind advanced mirrors can help in discovering new things in space and quantum physics?
12. Do you believe striving for perfection in mirror design is necessary for technological advancements?
13. How do you think the ELT’s mirrors will change the way we see the universe once it starts working in 2028?
14. Why or why not do you think it’s exciting that mirrors are helping make more powerful computer chips?
15. What impact do you think the ELT and the advanced mirrors will have on our knowledge of the universe in the future?
Individual Activities
📖💭 Vocabulary Meanings:
Match each word to its meaning.
Words:
1. Observatory
2. Optical
3. Hexagonal
4. Precise
5. Vibrations
6. Quantum
7. Secure
8. Transistors
9. Silicon
10. Efficient
11. Production
12. Advanced
13. Striving
14. Perfection
15. Expanding
Meanings:
(A) Working in a way that saves time and energy
(B) The state of being free from flaws or defects
(C) Making a great effort to achieve something
(D) Related to sight or vision
(E) A place equipped for observing celestial events
(F) Small electronic parts that control the flow of electricity
(G) Exact and accurate
(H) The process of making or creating something
(I) Having six sides and six angles
(J) Relating to the smallest particles of matter
(K) Highly developed or complex
(L) A chemical element used in making electronic circuits
(M) Increasing in size or scope
(N) Rapid movements back and forth
(O) Safe and protected from danger
Go to answers ⇩
🔡 Multiple Choice Questions:
1. What is the name of the biggest optical telescope being built in Chile’s Atacama desert?
(a) Super Huge Telescope (SHT)
(b) Extremely Large Telescope (ELT)
(c) Giant Optical Telescope (GOT)
(d) Massive Space Telescope (MST)
2. How many huge mirrors does the ELT have?
(a) Three
(b) Ten
(c) Seven
(d) Five
3. What is the main mirror of the ELT made up of?
(a) 798 smaller hexagonal pieces
(b) 500 smaller square pieces
(c) 1000 smaller triangular pieces
(d) 1200 smaller circular pieces
4. Who is in charge of ensuring the ELT’s mirrors are top-notch?
(a) Dr. Alex Johnson
(b) Dr. Elise Vernet
(c) Dr. Maria Lopez
(d) Dr. Thomas Smith
5. What is special about the M4 mirror?
(a) It can change its shape 1,000 times every second
(b) It can change its size
(c) It can rotate 360 degrees
(d) It can reflect light faster than any other mirror
6. Which institute has made a mirror at the tiniest level possible?
(a) NASA
(b) European Space Agency
(c) Max Planck Institute for Quantum Optics
(d) Harvard University
7. What is Zeiss working on in Oberkochen, Germany?
(a) Building rockets
(b) Developing new smartphones
(c) Designing cars
(d) Making super flat mirrors for computer chip production
8. What is Zeiss aiming to achieve by 2030 in terms of microchips?
(a) Create microchips with one million transistors
(b) Create microchips with one billion transistors
(c) Create microchips with one trillion transistors
(d) Create microchips with one hundred billion transistors
Go to answers ⇩
🕵️ True or False Questions:
1. Zeiss in Germany is working on making super flat mirrors for computer chip production.
2. The Max Planck Institute for Quantum Optics has created a mirror at the smallest possible level to explore quantum technology.
3. Outdated mirror technology is not only hindering computer chip production but also hindering space exploration and quantum physics research.
4. The ELT has five huge mirrors, with the main mirror being made up of 798 smaller hexagonal pieces.
5. Zeiss aims to create microchips with one trillion transistors by 2030.
6. Dr. Elise Vernet is not responsible for ensuring the ELT’s mirrors are of high quality.
7. The Extremely Large Telescope (ELT) is being built in Australia’s Outback desert and will be the world’s smallest optical telescope.
8. The M4 mirror in the ELT is the smallest flexible mirror ever made and cannot change its shape rapidly.
Go to answers ⇩
📝 Write a Summary:
Write a summary of this news article in two sentences.
Check your writing now with the best free AI for English writing!
Writing Questions:
Answer the following questions. Write as much as you can for each answer.
Check your answers with our free English writing assistant!
1. What is the Extremely Large Telescope (ELT) and where is it being built?
2. Who is Dr. Elise Vernet and what is her role in the ELT project?
3. What is special about the M4 mirror in the ELT?
4. What is Zeiss working on in Oberkochen, Germany, and why are super flat mirrors important?
5. How are advanced mirrors contributing to the future of technology and our understanding of the universe?
✅ Answers
🤔✅ Comprehension Question Answers:
1. What is the name of the telescope being built in Chile’s Atacama desert, and when is it expected to start working?
The telescope being built in Chile’s Atacama desert is called the Extremely Large Telescope (ELT), and it is expected to start working in 2028.
2. How many huge mirrors does the Extremely Large Telescope (ELT) have, and what are they made of?
The ELT has five huge mirrors, with the main mirror, M1, being made up of 798 smaller hexagonal pieces that work together as one.
3. Who is responsible for ensuring the ELT’s mirrors are of high quality?
Dr. Elise Vernet, who works at ESO, is responsible for ensuring the ELT’s mirrors are of high quality.
4. What is unique about the M4 mirror in the ELT?
The M4 mirror in the ELT is the biggest flexible mirror ever made, capable of changing its shape 1,000 times every second to deal with air movements and vibrations in the telescope.
5. What is the Max Planck Institute for Quantum Optics working on that involves mirrors?
The Max Planck Institute for Quantum Optics has made a mirror at the tiniest level possible, showing how quantum tech could be used in the future, like for secure data networks.
6. Where is Zeiss located, and what are they working on regarding mirrors?
Zeiss is located in Oberkochen, Germany, and they are working on making super flat mirrors crucial for machines used in making computer chips.
7. How do super flat mirrors made by Zeiss contribute to computer chip production?
Super flat mirrors made by Zeiss help print really small transistors on silicon wafers, making computer chip production more efficient.
8. How is the technology behind advanced mirrors impacting both computer chip production and the study of space and quantum physics?
The technology behind advanced mirrors is helping make more powerful computer chips and discover new things in space and quantum physics, pushing the limits of technology and expanding our knowledge of the universe.
Go back to questions ⇧
🎧✍️✅ Listen and Fill in the Gaps Answers:
(1) Large
(2) telescope
(3) hexagonal
(4) precise
(5) mirror
(6) mirrors
(7) flexible
(8) Institute
(9) quantum
(10) working
(11) making
(12) microchips
(13) amazing
(14) physics
(15) design
(16) knowledge
Go back to questions ⇧
📖💭✅ Vocabulary Meanings Answers:
1. Observatory
Answer: (E) A place equipped for observing celestial events
2. Optical
Answer: (D) Related to sight or vision
3. Hexagonal
Answer: (I) Having six sides and six angles
4. Precise
Answer: (G) Exact and accurate
5. Vibrations
Answer: (N) Rapid movements back and forth
6. Quantum
Answer: (J) Relating to the smallest particles of matter
7. Secure
Answer: (O) Safe and protected from danger
8. Transistors
Answer: (F) Small electronic parts that control the flow of electricity
9. Silicon
Answer: (L) A chemical element used in making electronic circuits
10. Efficient
Answer: (A) Working in a way that saves time and energy
11. Production
Answer: (H) The process of making or creating something
12. Advanced
Answer: (K) Highly developed or complex
13. Striving
Answer: (C) Making a great effort to achieve something
14. Perfection
Answer: (B) The state of being free from flaws or defects
15. Expanding
Answer: (M) Increasing in size or scope
Go back to questions ⇧
🔡✅ Multiple Choice Answers:
1. What is the name of the biggest optical telescope being built in Chile’s Atacama desert?
Answer: (b) Extremely Large Telescope (ELT)
2. How many huge mirrors does the ELT have?
Answer: (d) Five
3. What is the main mirror of the ELT made up of?
Answer: (a) 798 smaller hexagonal pieces
4. Who is in charge of ensuring the ELT’s mirrors are top-notch?
Answer: (b) Dr. Elise Vernet
5. What is special about the M4 mirror?
Answer: (a) It can change its shape 1,000 times every second
6. Which institute has made a mirror at the tiniest level possible?
Answer: (c) Max Planck Institute for Quantum Optics
7. What is Zeiss working on in Oberkochen, Germany?
Answer: (d) Making super flat mirrors for computer chip production
8. What is Zeiss aiming to achieve by 2030 in terms of microchips?
Answer: (c) Create microchips with one trillion transistors
Go back to questions ⇧
🕵️✅ True or False Answers:
1. Zeiss in Germany is working on making super flat mirrors for computer chip production. (Answer: True)
2. The Max Planck Institute for Quantum Optics has created a mirror at the smallest possible level to explore quantum technology. (Answer: True)
3. Outdated mirror technology is not only hindering computer chip production but also hindering space exploration and quantum physics research. (Answer: False)
4. The ELT has five huge mirrors, with the main mirror being made up of 798 smaller hexagonal pieces. (Answer: True)
5. Zeiss aims to create microchips with one trillion transistors by 2030. (Answer: True)
6. Dr. Elise Vernet is not responsible for ensuring the ELT’s mirrors are of high quality. (Answer: False)
7. The Extremely Large Telescope (ELT) is being built in Australia’s Outback desert and will be the world’s smallest optical telescope. (Answer: False)
8. The M4 mirror in the ELT is the smallest flexible mirror ever made and cannot change its shape rapidly. (Answer: False)
Go back to questions ⇧